Tool Overview
The new generation of acoustic tool (EPST) was designed to provide reservoir flow analysis (RFA), identify leaks and detect crossflow behind pipes. The tool incorporates a conventional spectral noise logging module (SNL) and a vector vibroacoustic logging module (VVL) which allows differentiation between horizontal and vertical components of flow. The tool can also be combined with a spinner.
Main Advantages
- Acoustic modules can be run in combination with a spinner to provide wellbore flow profile in a single intervention.
- The survey can be conducted in the presence of any type of fluid oil, water, gas.
- Presence or absence of cement behind pipes will not affect the data quality.
- The tool incorporates a gamma ray, temperature and pressure sensors and a casing collar locator (CCL)therefore capturing additional information in a single run.
- The presence of multidirectional sensors in the VVL module allows identification of horizontal and vertical components of flow.
The advantages listed above make this tool the most cost-effective flow profiling and leak detection tool in the market. Acoustic log data can be used to determine which zones are producing and which zones are not. This can give a clearer picture of the reservoir sweep efficiency and which zones are producing water. The tool can also identify fluid movement and crossflow behind the pipe, including channeling of fluids up into the annulus which could potentially cause well integrity issues. Depths of leaks in the pipe can also be detected. The results can then be used to determine if remedial action such as a water shut-off, scab liner etc. is required.
Challenge
Insufficient sweep efficiency can lead to inadequate pressure support to neighboring wells. Identifying zones which are not accepting injection fluid is key for planning remedial action to improve sweep efficiency and ultimately increase oil recovery.
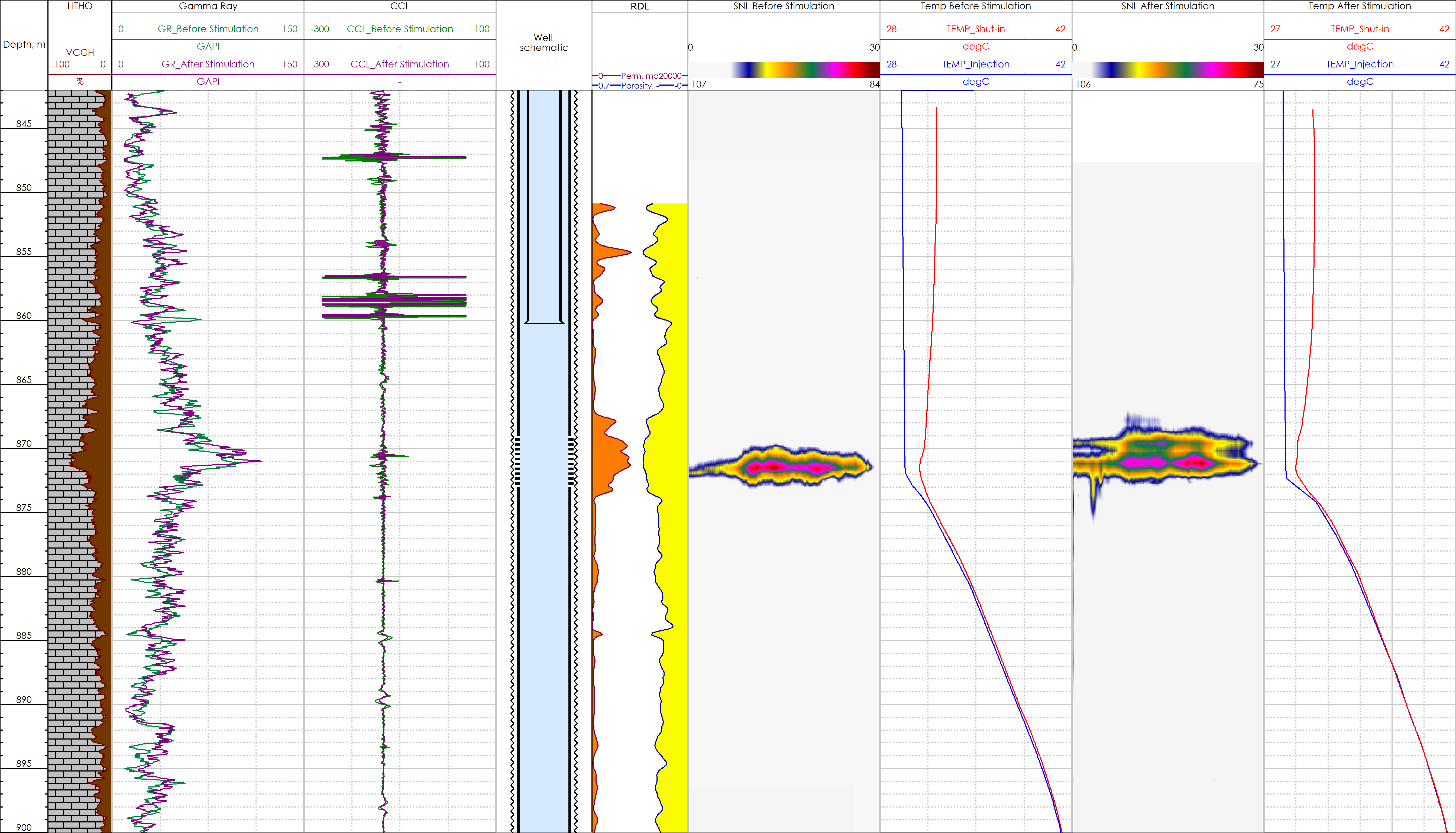
Acoustic Logging Result
One example of when acoustic logging was conducted to check acid stimulation efficiency is shown below:
The well was drilled in 2015 as a vertical water injector. The well was completed with a 9 5/8” surface casing and a 7” production casing. The 7” casing was perforated at 869-873 m to support the reservoir pressure in nearby production wells. The average injection rate was 200 m3/d. However, after 5 years of injection there was no improvement in pressure in the nearby production wells. It was decided to run an acoustic logging tool to identify the reservoir intake zones as the spinner tool can only identify the wellbore intake zones i.e., into the perforations and not flow behind the casing.
The SNL data together with the shut-in temperature curve indicated that all the injected water went into a very narrow interval of 1 m with a sweeping efficiency of 25% of the total perforated interval. This narrow zone correlates to a high permeability layer. Based on the acoustic log results it was decided to perform an acid stimulation of the perforated interval to improve sweep efficiency. After the acid stimulation the well was put on injection for 5 months. The acoustic log was then repeated. The SNL data indicated that after stimulation an extra intake interval was evident which was also confirmed by the temperature curve. This demonstrates that the acid stimulation was successful in improving the sweep efficiency. In addition, the SNL data showed a downward crossflow below the bottom of the perforated interval.
Conclusion
Acoustic logging is a powerful technique to provide accurate reservoir flow behaviors behind the casing which would otherwise be missed if only using spinner data. This can aid the Client to determine how to improve sweep efficiency and improve 3D dynamic modelling.
More case studies
Looking for more information?
Get in touch with us and our representative will get back to you
Contact Us